Calculating Cycle Times: Boost Manufacturing Efficiency
Learn how calculating cycle times can optimize your production. Discover expert strategies to identify bottlenecks and improve efficiency today.
Learn how to reduce lead time and improve efficiency with expert strategies. Boost your supply chain performance today!
In manufacturing, lead time is the time it takes from when a customer places an order to when they receive it. This metric significantly influences profitability and customer satisfaction. It's a critical factor that can make or break a business. This section explores the advantages of reducing lead time.
Reducing lead time improves efficiency and lowers operational costs. Faster production cycles often mean lower expenses. Shorter lead times also minimize inventory holdings, freeing up capital.
Less money tied up in stored goods translates to reduced warehousing expenses. Streamlined processes also help minimize waste and maximize how you use resources, directly improving profit margins.
Customer satisfaction is crucial. Long lead times can frustrate customers, leading to lost sales. Consistently fast deliveries build customer loyalty.
Loyal customers lead to repeat business and positive referrals. This boosts brand reputation and market share. Reducing lead time is a cornerstone of a thriving manufacturing business.
Speed is key in today's business world. Reducing your lead time allows you to respond to market demands faster than competitors. This agility helps you capitalize on opportunities and gain market share.
Shorter lead times also provide flexibility for customization, meeting specific customer needs and strengthening your competitive advantage. Being adaptable is crucial in a fluctuating market.
Understanding your current lead time is the first step to improvement. Track key metrics like order lead time (order placement to delivery), production lead time (manufacturing time), and material lead time (time to receive supplies).
Analyzing this data helps pinpoint areas for improvement, like identifying bottlenecks and optimizing processes. Data-driven strategies for lead time reduction inform decisions that impact your business's overall performance. Almost 40% of industrial resources are wasted due to bottlenecks, resulting in a $12 trillion loss globally. Explore this topic further. This highlights the crucial need for optimized production.
Before you can reduce lead time, you need to understand where your current processes are faltering. This requires a thorough examination of your production flow to find those hidden bottlenecks that quietly sabotage your efficiency. This section explores practical strategies for pinpointing these time traps, so you can implement targeted solutions for maximum impact.
Effective bottleneck detection starts with accurate data. Time studies, conducted on each stage of your production process, provide the raw numbers needed to identify slowdowns. It’s not just about measuring how long each task takes; it's about understanding the variations in those times and the underlying causes.
Value stream mapping visualizes your entire production flow, from raw materials to finished goods. This big-picture view makes it easier to spot where work piles up or processes stall. By mapping the flow of materials and information, you can find hidden waste and areas for streamlining.
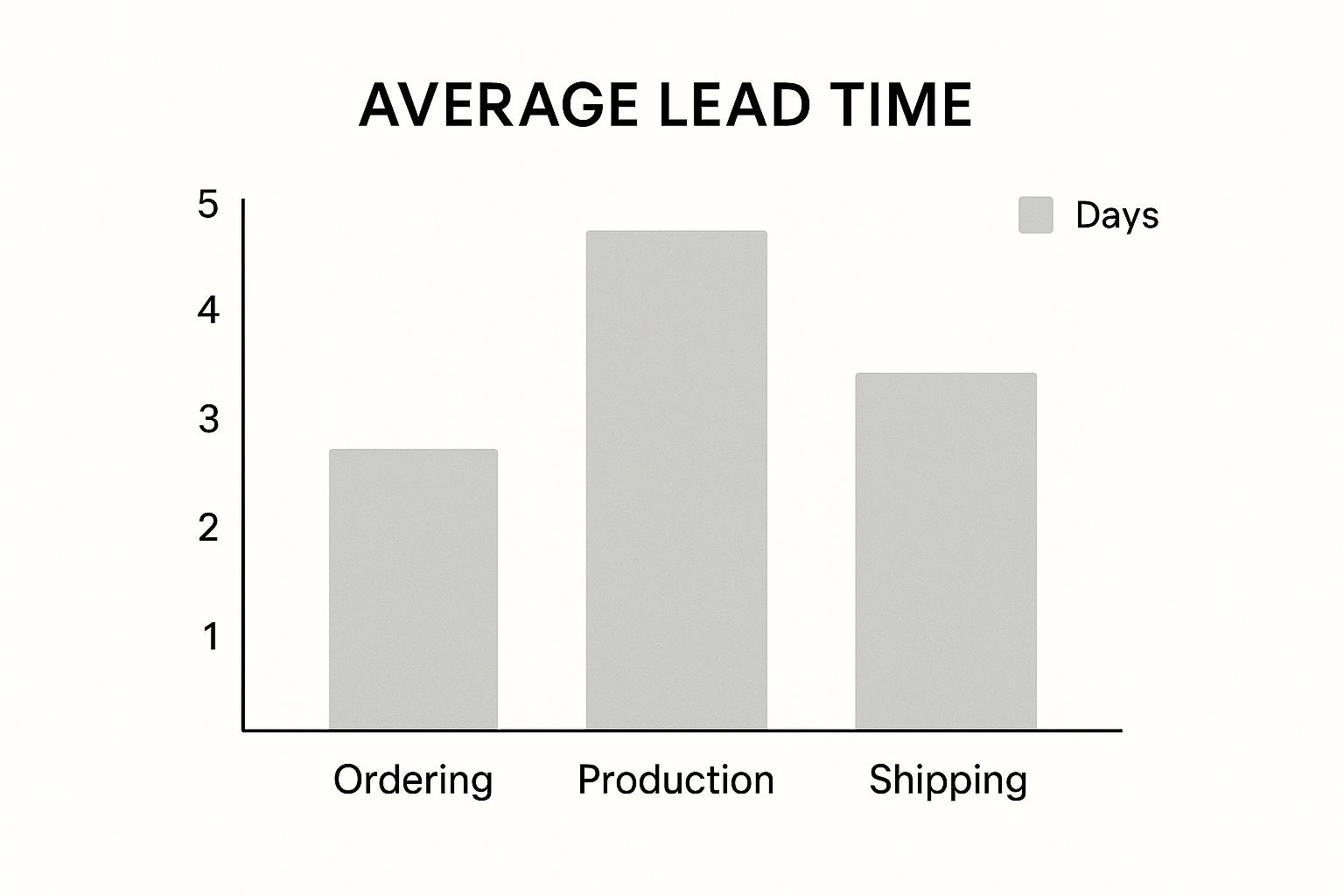
The infographic above breaks down average lead times across ordering, production, and shipping. The production phase represents the majority of the lead time, highlighting a significant area for potential optimization. Addressing bottlenecks within production is crucial for meaningful lead time reduction.
Not all bottlenecks are the same. Systematic bottlenecks are recurring issues embedded in your processes, like limited equipment capacity or a poorly designed workflow. These chronic problems need long-term solutions.
Temporary bottlenecks are short-term disruptions, such as equipment malfunction or a sudden increase in orders. These temporary issues can still affect lead time but require different approaches, focusing on quick solutions and backup plans. Distinguishing between these two is crucial for allocating resources effectively.
After identifying your bottlenecks, the next step is prioritization. Consider the financial impact of each bottleneck and the effort needed to fix it.
For instance, a bottleneck causing significant production delays and affecting a high-volume product should be addressed first, even if it requires a more complex solution. This targeted approach ensures your resources are focused where they'll have the greatest impact on lead time reduction. Prioritizing the most impactful bottlenecks streamlines your improvement efforts and maximizes your gains.
To understand common bottlenecks across various industries, let's examine the following table:
Common Lead Time Bottlenecks Across Industries
This table identifies typical bottlenecks that extend lead times and their relative impact across different sectors.
| Bottleneck Type | Manufacturing Impact | Service Industry Impact | Retail Impact | Potential Time Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Shortages | Production halts, delayed orders | Inability to fulfill service requests | Stockouts, lost sales | Days to weeks |
| Supplier Delays | Production slowdowns, increased lead times | Service delivery delays, customer dissatisfaction | Inventory gaps, missed promotions | Days to weeks |
| Equipment Malfunction | Production downtime, reduced output | Service disruptions, decreased capacity | In-store operations hampered, customer inconvenience | Hours to days |
| Inefficient Processes | Increased cycle times, wasted resources | Slow service delivery, reduced efficiency | Checkout delays, decreased customer throughput | Hours to days |
| Inadequate Staffing | Reduced production capacity, missed deadlines | Long wait times, poor customer service | Understaffed stores, lost sales opportunities | Hours to weeks |
Key Insights:
By understanding these common bottlenecks and their potential impact, businesses can proactively implement strategies to mitigate their effects and optimize lead times.

Let's explore practical lean manufacturing strategies that genuinely reduce lead time. These methods, proven effective by successful operations leaders, deliver tangible results. This involves shifting from abstract ideas to concrete actions that optimize production.
Just-In-Time (JIT) production, a core principle of lean manufacturing, centers on producing goods only when required. This minimizes inventory costs and reduces waste. JIT demands careful planning and coordination to ensure materials arrive precisely when the production process needs them.
Working in tandem with JIT, Kanban systems offer a visual tool for managing workflow. Using cards or signals, Kanban visually represents the stages of work and inventory levels. This allows for real-time production adjustments based on actual demand, further minimizing delays.
5S, a workplace organization methodology, optimizes efficiency by reducing wasted time and movement. The five steps of this system are: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
These steps establish a structured, clean, and efficient work environment. For instance, organizing tools and materials reduces search time, contributing to smoother workflows and quicker production. This organized environment minimizes distractions and maximizes productive work time.
Visual management tools enhance communication and transparency within the production process. These techniques use visual cues, such as charts and dashboards, to display key performance indicators (KPIs) and process status.
This immediate visibility allows teams to quickly identify and address bottlenecks. Moreover, visual management promotes accountability and helps maintain improvements. This proactive approach helps identify and resolve potential issues before they cause major delays.
Implementing lean strategies presents certain difficulties. Resistance to change, insufficient training, and maintaining progress are common hurdles. You might be interested in: How to master....
However, successful manufacturers overcome these challenges through open communication, employee engagement, and diligent data tracking. By establishing achievable goals and celebrating small victories, companies build a culture of continuous improvement. The application of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning has also become a key strategy for reducing lead times. Analyzing historical and real-time data allows these technologies to predict demand fluctuations. This lets companies adapt production and supply chain operations. This approach has been particularly effective in industries with significant demand variations. Find more detailed statistics here. Data analysis ensures the lean manufacturing process is constantly optimized for maximum effectiveness.
Your supply chain has a significant impact on your lead time. While internal processes are essential, a slow or unreliable supply chain can undermine any internal efficiencies you've gained. This section explores how to create a responsive supplier network that empowers you to reduce lead times.
Choosing suppliers solely on price can be a costly mistake. Cost is definitely a factor, but prioritizing suppliers committed to speed and reliability is crucial. This means assessing their history of on-time deliveries and their capacity to adapt to changing needs. A consistently late supplier, even with lower prices, ultimately increases your lead time and risks damaging customer relationships. Seek suppliers who view themselves as partners invested in your success.
Inventory management is a key factor in lead time reduction. Too much inventory ties up capital and increases storage expenses, but too little can cause production delays. The sweet spot is finding the right balance. Implement inventory optimization strategies that support your lead time goals. Demand forecasting helps anticipate future needs, allowing you to maintain optimal inventory levels without excess. This involves examining past sales, market trends, and other factors to predict demand and adjust inventory proactively.
For true supply chain agility, effective communication is paramount. Establish clear communication channels with your suppliers to maintain visibility and avoid surprises. Implement systems for real-time information sharing on order status, potential delays, and other important updates. System integration with your suppliers, for example, can automate updates, minimizing manual communication. This transparency builds trust and enables proactive adjustments to your production schedule when necessary. Reducing lead times has become increasingly important worldwide as customer expectations for fast delivery grow. Companies like Becton Dickinson (BD) have achieved lead time reductions of up to 60% in some overseas markets, helping them prioritize urgent customer needs. Explore this topic further.
Negotiating favorable terms doesn't equate to squeezing suppliers for the lowest possible price. Instead, focus on nurturing long-term partnerships based on mutual benefit. Consider agreeing on guaranteed lead times, prioritized order fulfillment, or joint inventory management. A strong supplier relationship is a valuable asset in reducing lead time. Open communication and a collaborative spirit can lead to innovative solutions that benefit everyone.
Disruptions can occur even with the best laid plans. Develop contingency plans to address potential supply chain disruptions. This includes identifying backup suppliers, holding safety stock for vital components, and creating adaptable production schedules. Being prepared for unforeseen events minimizes the impact on your lead time and preserves customer satisfaction. This proactive risk management approach is vital for sustained success.
The following table offers a comparison of different supply chain strategies and their typical effect on lead time reduction.
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity | Cost | Typical Lead Time Reduction | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Collaboration | Moderate | Moderate | 10-30% | Businesses with strong supplier relationships |
| Inventory Optimization | Moderate | Low to Moderate | 5-15% | Businesses with predictable demand |
| Process Automation | High | High | 20-40% | Large businesses with complex processes |
| Demand Forecasting | Moderate | Low to Moderate | 5-20% | Businesses with seasonal or fluctuating demand |
| Transportation Optimization | Moderate | Moderate | 5-15% | Businesses with complex shipping logistics |
This comparison helps businesses choose the best approach for their needs. By understanding the complexity, cost, and potential lead time reduction of each strategy, manufacturers can make informed choices to optimize their supply chains for faster, more efficient delivery.

Understanding which technologies truly impact production lead times is essential for manufacturers. This section explores how smart automation can significantly improve speed and efficiency.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) bring precision to production scheduling. They replace guesswork with data-driven decisions, tracking real-time production information for accurate insights into each manufacturing stage. This allows for dynamic schedule adjustments, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing delays.
For instance, if a machine unexpectedly malfunctions, the MES can automatically reroute tasks to another available machine. This prevents bottlenecks and keeps production flowing.
Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets or processes. Companies use them to simulate potential changes in a risk-free environment. This allows manufacturers to identify problems and refine processes before real-world implementation, avoiding expensive on-the-floor experimentation.
Imagine testing a new factory layout virtually. A digital twin can reveal potential bottlenecks or layout inefficiencies before they disrupt production, significantly reducing the risk of extended lead times.
Equipment breakdowns can severely disrupt production and dramatically increase lead times. AI-powered predictive maintenance offers a solution. AI algorithms analyze data from sensors and other sources to predict potential equipment failures.
This allows for proactive maintenance before a breakdown, minimizing downtime and preventing costly delays. For example, AI might predict when a crucial machine requires service based on its usage patterns, enabling scheduled maintenance that minimizes production impact.
Choosing the right technology for lead time reduction depends on your business size and specific needs. Implementing a full-scale MES system may be excessive for a small manufacturer.
For smaller businesses, focusing on improving communication with suppliers or implementing basic process automation might yield a higher return on investment. Larger companies with intricate production processes may benefit from sophisticated tools like digital twins and AI-powered predictive maintenance.
Learn more about selecting appropriate solutions in our article on choosing the right technology for your business. Consider implementation challenges and the potential return on investment. Assessing these factors will ensure you select the technologies that deliver the best results.
Reducing lead time doesn't always require a huge budget. Many manufacturers see significant improvements through smart, low-cost process refinements. Let's explore some of these "quick wins" that can deliver a substantial return on investment without emptying your pockets.
Cross-training allows your employees to handle multiple roles within the production process. This flexibility minimizes bottlenecks when someone is out. Imagine your main milling machine operator is absent. A cross-trained employee can step in, keeping production moving. This agility makes your workforce more resilient and keeps things running smoothly.
Communication delays can silently add to lead times. Simple improvements to your communication systems can make a big impact. Using readily available project management software can create a central hub for information, minimizing miscommunication and ensuring everyone stays up-to-date. Clear communication means faster decisions and a quicker production cycle.
The layout of your production floor has a direct impact on efficiency. Analyze your current setup to find ways to reduce movement and streamline material flow. Even something as simple as relocating a frequently used tool closer to the workstation can shave valuable seconds off each task, accumulating significant time savings over the long run. This reduces wasted motion and speeds up production. Rearranging workstations to follow the natural flow of the production process can also yield impressive results.
Process changes only work with employee support. Clearly communicate the benefits of lead time reduction to your team and involve them in the process. Getting their feedback and addressing their concerns builds a sense of ownership. This collaborative approach makes successful implementation and ongoing improvement more likely. When employees understand the reasons behind changes, they’re more likely to embrace them.
Reducing lead time shouldn't mean sacrificing quality. Successful manufacturers find the balance. Integrating quality checks throughout production, instead of relying only on final inspection, is key. This ongoing monitoring catches defects early, minimizing rework and preventing costly delays. Addressing quality proactively avoids time-consuming corrections later, allowing you to reduce lead time while upholding high standards. Maintaining quality throughout the process is essential for achieving both speed and excellence.
Reducing lead time isn't a one-time fix; it requires ongoing dedication. Unfortunately, many improvements disappear within months. This section explores building a culture of continuous improvement to sustain lead time reduction over the long haul. Interested in learning more about us? Learn more about us.
Effective metrics are essential for lead time reduction. Go beyond simply measuring overall lead time. Track individual components like production lead time, material lead time, and order processing time. This detailed approach pinpoints slowdowns.
Regularly review these metrics for trends and deviations. A small increase in material lead time one month might not be significant. However, a consistent increase over several months signals a deeper problem that needs investigation.
Establish regular reviews of lead time performance. These could be weekly meetings with supervisors, monthly reviews with department heads, or quarterly reviews with senior management.
These reviews aren't just about numbers. They're about identifying challenges, brainstorming solutions, and reinforcing the importance of continuous improvement. This focus keeps lead time reduction a priority.
When lead times increase, don't just address the symptoms. Conduct a root cause analysis to find the underlying problems. This might involve techniques like the 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams.
For example, if a machine malfunction caused a delay, ask "why did the machine malfunction?" The answer might reveal a lack of preventative maintenance. This approach addresses the core problem.
Visual management systems, like Kanban boards and Andon systems, make performance visible. These visual cues provide real-time feedback on production, highlighting bottlenecks and areas needing attention.
This transparency promotes accountability and empowers employees. When everyone sees the impact of their work on lead time, it creates shared responsibility for continuous improvement.
Recognizing and celebrating successes is crucial for team motivation. Acknowledge small wins and major milestones. This could involve highlighting improvements during meetings, offering bonuses for achieving goals, or simply expressing appreciation.
Celebrating success reinforces positive behavior and keeps the team engaged in the ongoing effort.
Lead time reduction is important, but it shouldn't compromise other objectives like quality and cost control. Create a framework that balances these priorities.
This could involve setting targets for all three areas and tracking them. For example, a goal might be to reduce lead time by 15% while maintaining a 98% on-time delivery rate and staying within budget.
Focus on long-term strategies for lasting change. This might include investing in automation, redesigning workflows, or implementing new technologies. These initiatives take time and resources, but they build a foundation for sustained improvement.
Think of this as building a more efficient engine, not just a temporary boost. This strategic approach ensures long-term benefits.
Ready to empower your agile team with real-time insights? Explore how Umano can help you achieve your goals.
Learn how calculating cycle times can optimize your production. Discover expert strategies to identify bottlenecks and improve efficiency today.
Learn the cycle time definition and how to optimize this vital metric to boost manufacturing efficiency and drive growth.
Learn key strategies to improve agile cycle time, enhance delivery speed, and maximize team productivity for better project outcomes.
Be the first to know about new B2B SaaS Marketing insights to build or refine your marketing function with the tools and knowledge of today’s industry.